Properly composed nutrition will allow you to forget about the unbearable pain in the joints and lead a full life. We talk about the diet for gout: what is useful and what is not.

Gout is a systemic chronic metabolic disease that causes inflammation, swelling, and pain in the joints. The disease is associated with the accumulation and retention in the body of uric acid salts - urates. Gout has been known since ancient times, and its main symptoms were described by ancient doctors. Many famous people suffered from gout, for example Alexander the Great, emperors and empresses, the English king Henry VIII, the German scientist Gottfried Leibniz, the philosophers Voltaire Kant and Schopenhauer.
Gout is still a very common disease. Most often this disease affects men. The age at which the first flare-up usually occurs is between 35 and 45 years for men and 45 and 50 years for women.
gout symptoms
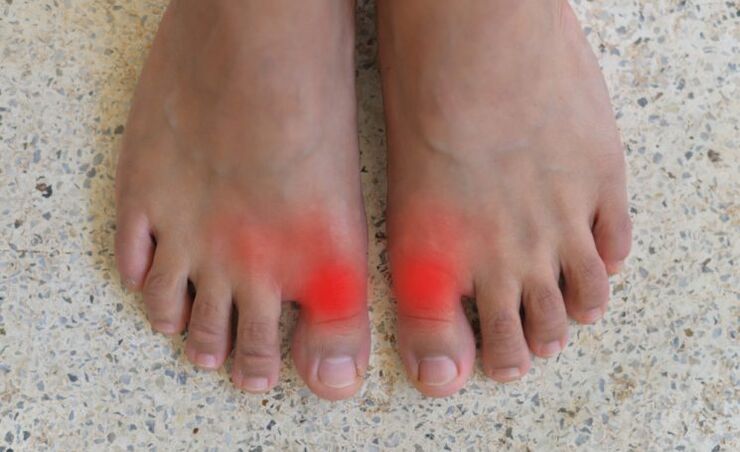
A characteristic sign of gout is the formation of so-called tophi (deposits of uric acid salts in the form of nodules and bumps in the connective tissue). Gout sufferers complain of acute pain in the joints – the big toe is most commonly affected. From the ancient Greek language, the name of the disease is translated as "leg in a trap", since most often patients are concerned about acute pain in the ankles. The pain intensity increases rapidly and reaches a peak after about 24-48 hours. The joint area is redand swollen. Body temperature may rise, chills appear. Gout attacks are also uncomfortable because they limit the patient's movement. If you do not resort to appropriate treatment, the acute phase lasts about a week, then the symptoms gradually subside. Goutcan progress: pain attacks become more frequent, new joints, for example, elbows, hands, are involved in the pathological process. As a result of the growth and enlargement of the nodes, the joints are deformed, their mobility and functionality are impaired. And this leads to problems with movement: the patientbecomes less mobile. In later stages, gout can developlead to urolithiasis.
Depending on the course, the disease can be acute (acute gouty arthritis) or chronic (recurrent arthritis). There are also atypical forms of gout, for example, pseudophlegmonous, asthenic, rheumatoid, etc. They are much less common.
Reasons for the development of the disease
As we have already said, gout occurs when a lot of uric acid is formed in the body and is not eliminated from the body in a timely manner. A variety of factors can contribute to this. Here are the main causes of high uric acid levels and the development of gout.
- hereditary predisposition. Most often it manifests itself in the form of various genetic disorders, in which the amount of one or another enzyme in the body is reduced.
- Increased absorption of purine bases in the body. These substances are contained in the DNA and RNA of living organisms and are involved in the transmission of genetic information. Purine bases enter the body with food, drink and also when the body's own cells break down. In the Middle Ages, gout was called the "disease of kings". This is explained by the nobility's fondness for plentiful meals. The body of those who abused meat and alcohol (and there are, first of all, purines) could not cope with the huge concentration of uric acid. Ordinary people ate poorly, mainly plant foods, and therefore rarely suffered from gout.
- Problems with the elimination of uric acid in the urine. Usually seen in chronic kidney disease. It is generally accepted that gout in such cases is secondary, that is, it is a consequence of another disease. If it is eliminated, the gout will also disappear.
Treatment and prevention of gout
The success of treating gout is an integrated approach. If possible, specialists try to determine the cause of the disease and eliminate it. However, this is not always possible, so one must limit oneself to symptomatic treatment aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease and improving the quality of life of a gouty patient.
The main directions in the treatment of gout
- Medical treatmentwith anti-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory drugs. Anti-inflammatory drugs are primarily taken during an exacerbation to reduce pain and swelling. Antigout - long, sometimes lifelong. This is a group of drugs that directly affect the metabolism of purine bases and uric acid in the body.
- local treatment.It is prescribed both during remission and during exacerbation. It consists of the use of compresses with painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as physiotherapeutic procedures. During the period of remission, applications with paraffin and medicinal mud are useful - this will help eliminate uric acid and improve joint mobility.
- Surgery.Allocate with a strong growth of nodes and cones. They are removed to avoid severe deformation of the joints and limit their mobility.
- Diet.Diet plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of gout. The main goal of such a diet is to reduce the level of uric acid compounds in the body. If the therapeutic and prophylactic diet is followed, purine bases practically do not enter the body from the outside, and the level of uric acid decreases. By limiting consumption or eliminating certain foods from our diet, we prevent the disease from developing and postpone the next flare-up. It is recommended to follow a therapeutic and prophylactic diet for gout patients throughout life, and not only during periods of exacerbation.
How to go on a diet

As a basis for gout, experts recommend nutritional table No. 6. This therapeutic and preventive diet was developed by a well-known nutritionist for patients with diseases associated with accumulation of uric acid in the body: gout, urolithiasis and uric acid diathesis. All of these ailments are metabolic diseases and cause serious complications. A special diet will help reduce the concentration of uric acid in the blood and normalize metabolism in the body. With a special diet, it is possible to reduce the formation of uric acid and the accumulation of urate in the kidneys and joint spaces. Diet also prevents the accumulation of purine bases that lead to gout. If you stick to it, you can quickly improve your general condition, reduce pain and discomfort in the joints.
Features of the diet table number 6
Therapeutic nutrition is balanced in terms of chemical composition and calorie content of products, sufficient in terms of minerals, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Energy intensity is 2700–3000 kcal. If you are overweight, it is recommended to reduce total calories by reducing carbohydrates.
- The amount of fat is 80-90 g per day. Fats of vegetable origin should be preferred, the source of which is vegetable oils.
- The daily amount of protein is 70-80 g, with at least half of the specified amount coming from plant-based protein foods.
- The amount of carbohydrates is 380-400 g per day with a normal body weight. With overweight and obesity, the amount of carbohydrates is reduced to 250-300 g per day.
- The amount of salt should not exceed 10 g per day.
- The daily amount of liquid should not exceed 1. 5-2 liters (excluding first courses).
The diet for gout does not imply strict restrictions, so it is usually well tolerated. Food should be boiled, baked, stewed. Try to avoid roasts. It causes the formation of a large number of extracts and carcinogens that adversely affect the digestive, urinary and cardiovascular systems. You need to eat fractionally every 2-3 hours in moderate portions without overeating.
Allowed foods for gout
The basis of the therapeutic diet for gout are alkaline foods: they normalize the metabolism of purine bases, and also reduce the amount of uric acid.
What can you eat with gout?
- Any kind of vegetables - both fresh and thermally processed.
- Baked goods made from rye and wheat flour, as well as with the addition of wheat bran.
- First courses cooked in a weak vegetable and fish broth, vegetarian okroshka, beetroot, lean cucumber and cabbage soup without meat.
- Dairy and sour milk products: low-fat kefir, sour milk, whole milk, low-fat sour cream, natural yogurt, fermented baked milk and low-fat cottage cheese.
- Fresh and thermally processed fruits and berries.
- Green and black tea with lemon, honey and milk. Homemade fruit and berry kisses, vegetable and fruit juices, berry fruit drinks. Herbal infusions (from chamomile blossoms, rose hips), fruit compotes, chicory.
- Desserts and sweets: natural honey, marshmallow, natural jam, berry jam, marmalade, homemade marshmallows.
- Fats: Refined sunflower, corn, olive, linseed oil. Butter is also allowed.
The foods and foods listed are considered safe for gout. There are also a number of products that you cannot exclude from the menu, but limit their use.
- Quail eggs and chicken eggs boiled in the form of steam omelets, hard-boiled or soft-boiled (no more than 1 egg per day).
- Of meat products, it is allowed to eat veal, lean beef, rabbit, turkey and chicken. From fish - fish of dietary varieties. Meat and fish dishes should be eaten no more than three times a week, preferably cooked. Thanks to this method of heat treatment, meat and fish are cleaned of purine bases, extracts and uric acid fragments.
- It is recommended to keep pasta to a minimum.
What not to eat with gout
Your diet should not include foods that contain large amounts of purine bases and uric acid. Here are foods not recommended for gout.
- Alcoholic and carbonated beverages.
- chocolate, cocoa.
- First courses cooked in meat and strong fish broth.
- All kinds of nuts and legumes, grape juice.
- Hard and pickled cheese.
- Sausages, smoked products, sausages, canned fish and meat, offal and meat and fish ingredients with a high fat content.
- All kinds of appetizers, pies, sauces, spices, condiments, ketchups, mayonnaise, mustard, grated horseradish root.
- Products from puff pastry and pastries, cakes, chocolate and caramel candies.
Sample menu for the week

Here is a sample menu for seven days for people with gout. It can be customized according to your preferences.
Monday
Breakfast:vegetable salad with vegetable oil (sunflower, corn or olive); 1 soft-boiled chicken egg; pumpkin or carrot juice.
Having lunch:pumpkin baked with honey; a glass of whole milk or natural yoghurt.
Dinner:boiled chicken breast with vegetable stew; a glass of orange or apple juice.
Afternoon snack:vegetarian borscht with potatoes; boiled fish fillet; weak green tea or rosehip drink.
Dinner:vegetarian cabbage roulade; fruit and berry jelly; low-fat cottage cheese with the addition of dried fruits.
Before going to bed, you can drink a glass of milk or low-fat kefir.
Tuesday
Breakfast:Scrambled eggs with vegetable salad seasoned with vegetable oil (corn, olive or sunflower), a glass of fruit or vegetable juice.
Having lunch:fruit or vegetable puree; Cottage cheese mass with the addition of dried fruits; a glass of herbal tea.
Dinner:braised zucchini with fresh herbs; Mashed potatoes; Vegetable salad, black or green tea.
Afternoon snack:a serving of fresh berries or fruit; Milkshake or a glass of whole milk.
Dinner:Cottage cheese with the addition of berry jam or dried fruit; Compote of berries and fruits.
the Wednesday
Breakfast:boiled rice porridge with the addition of grated apple; weak black or green tea.
Having lunch:a portion of fruit salad seasoned with natural yoghurt.
Dinner:vegetarian cabbage soup; pumpkin chops; a glass of whole milk
Afternoon snack:a glass of fermented baked milk or kefir; portion of berries.
Dinner:pancakes with fruit filling; Fruit and berry compote.
Thursday
Breakfast:cottage cheese and carrot casserole; Porridge; fruit compote.
Having lunch:homemade pasta cooked in milk.
Dinner:steamed beef chops with steamed cabbage; boiled buckwheat porridge, pumpkin juice.
Afternoon snack:carrot juice.
Dinner:Salad of boiled beets and carrots seasoned with olive oil; fruit jelly.
Friday
Breakfast:curd soufflé; fruit or vegetable juice.
Having lunch:Natural yoghurt with added wheat bran.
Dinner:cabbage and grated carrot salad; vegetarian soup; tomato juice.
Afternoon snack:Gummy bears or a portion of fruit.
Dinner:backed vegetables; Oatmeal, weak green or black tea.
Saturday
Breakfast:Steam Cheesecake; Natural yoghurt; fruit jelly.
Having lunch:Corn or oatmeal with milk.
Dinner:stewed diet fish with mashed potatoes; vegetarian soup with zucchini; weak black tea with lemon.
Afternoon snack:berry or milkshake.
Dinner:Vegetable salad; porridge from corn grits; Pumpkin, apple or carrot juice.
Sunday
Breakfast:Vegetable salad; a slice of bread with bran; rosehip drink.
Having lunch:Carrot and pumpkin salad, 1 soft-boiled chicken egg.
Dinner:Potato cutlets with the addition of grated zucchini; homemade pasta cooked in milk; fruit jelly.
Afternoon snack:Cottage cheese casserole with fruit.
Dinner:vegetable cabbage rolls; a glass of whole milk or low-fat kefir.
recipes
Vegetarian vegetable borsch
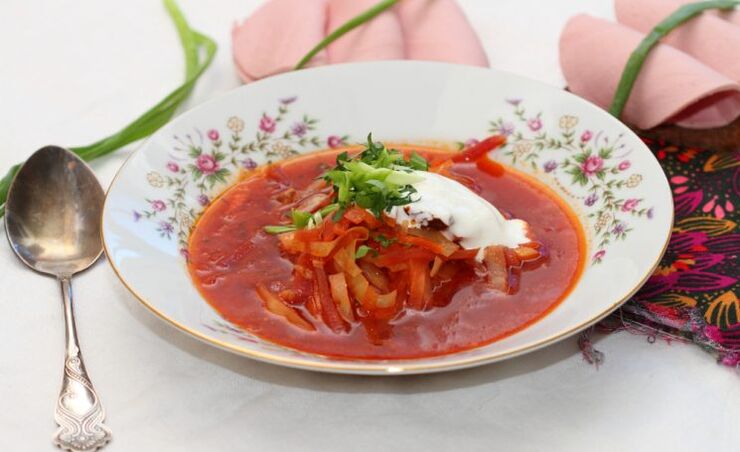

Ingredients:2. 5 liters of water, 1 onion, 2 carrots, 1 beetroot, 1 tomato, 1 celery root or stick, 2 potatoes, 200 g white cabbage, salt, pepper - to taste, herbs (dill, parsley), low-fat sour cream orNatural yoghurt - for serving.
Instruction.Add vegetables cut into small cubes or grated on a coarse grater to boiling water: onions, carrots, celery, beets, potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes (without peel). Cook until the vegetables are done. salt, seasoning. Then add finely chopped vegetables. Remove the pot from the stove and let the borscht steep. Serve with sour cream or yogurt (optional). In the finished borscht, you can put a piece of lean boiled beef.
Omelet with poultry or meat
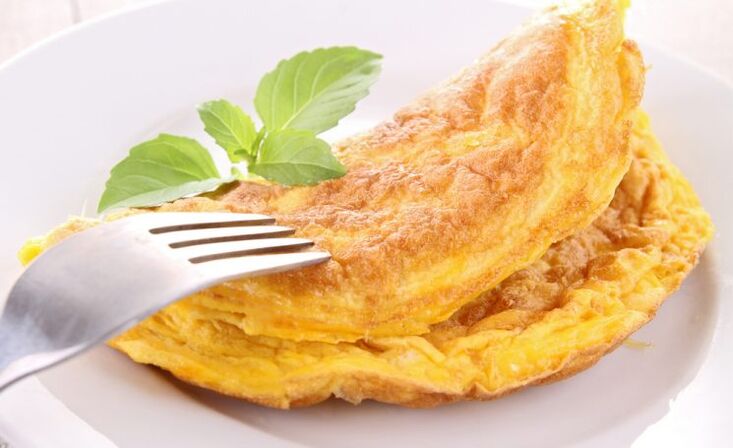

Ingredients:Turkey breast fillet (chicken, guinea fowl) without skin or lean table meat (beef, veal), 2 eggs, 2 tbsp. l. low-fat milk, salt to taste.
Instruction.Whisk eggs with milk. Salt. Pour pieces of cooked or baked poultry (meat) over the batter. Cook on both sides in the microwave, slow cooker, or deep skillet.
Boiled cod

Ingredients:500 g cod fillet, 1 tsp. lemon juice, 1 onion, 1 bay leaf, 1 tbsp. l. Olive oil, parsley root (to taste), peppercorns (4-5 peas), herbs (dill, parsley) - 1 tbsp. l. , salt to taste.
Instruction.Rinse the fillet in cold water with the addition of lemon and cut into portions. Put the pieces in the broth boiling with roots and spices so that the water covers the fish. Simmer the cod under the lid for 12 minutes. Serve with vegetable stew.
Carrot, apple and pumpkin salad

Ingredients:100 g fresh pumpkin, 1 medium carrot, 1 green apple, 1 tsp. lemon juice, 2-3 slices of orange or tangerine.
Instruction.Grate the vegetables on a coarse grater, mix. Add lemon juice and garnish the salad with orange (tangerine) slices.
Zander rolls with Chinese cabbage

Ingredients:500 g zander, 200 g cottage cheese (5%), 4 egg whites, 1 green Chinese cabbage, salt and pepper to taste.
Instruction.Grind with a blender or pass the pike perch fillet through a meat grinder twice. Then mix with cottage cheese. Beat the egg whites and add to the mass, mix, salt, pepper. Divide the ground beef into 4 portions and place each on a separate sheet of aluminum foil greased with olive oil. Roll up into a roll, pinning edges. Boil in a water bath for 10-14 minutes. Wash the cabbage, disassemble into leaves, salt, pepper and cook in a water bath for 10 minutes. Put the cabbage leaves on a plate, take the zander rolls out of foil and place them on top.
vegetable stew

Ingredients:1 onion, 1 carrot, 1 tomato, 200 g white cabbage, 1 potato, 1 pepper, 100 g small corn, 1 tbsp. l. Vegetable oil, herbs (dill, parsley, celery), salt, pepper to taste.
Instruction.Put finely chopped onion, grated carrots, peeled and chopped tomatoes in a saucepan heated with oil. Save easily. Then add the cabbage and the potatoes cut into squares and the corn. Stir, add some water, cover and simmer until done. Five minutes before readiness, add pepper and finely chopped greens.
vegetable casserole
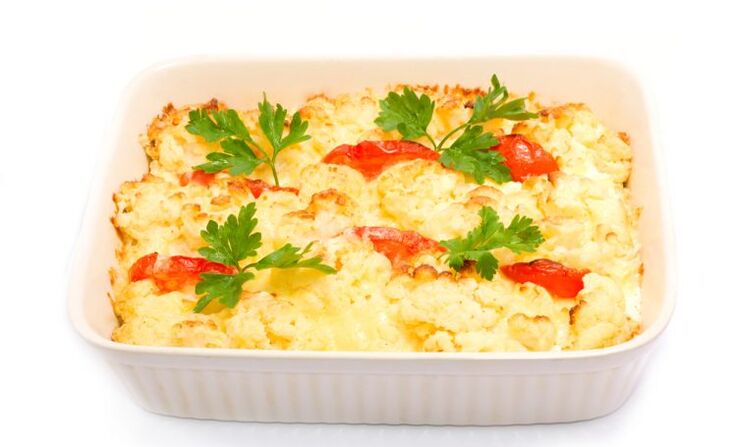

Ingredients:1 onion, 1 carrot, 300 g cauliflower, 1 potato, 1-2 eggs, herbs (dill, parsley, celery), salt and pepper to taste.
Instruction.In a deep baking dish greased with olive oil, put a vegetable mixture: finely chopped onions and carrots, cabbage and potatoes cut into squares. Stir, add finely chopped greens, pepper, salt and beaten eggs. Put in an oven preheated to 200 degrees. Bake for 20-25 minutes.
Zucchini rolls with cottage cheese
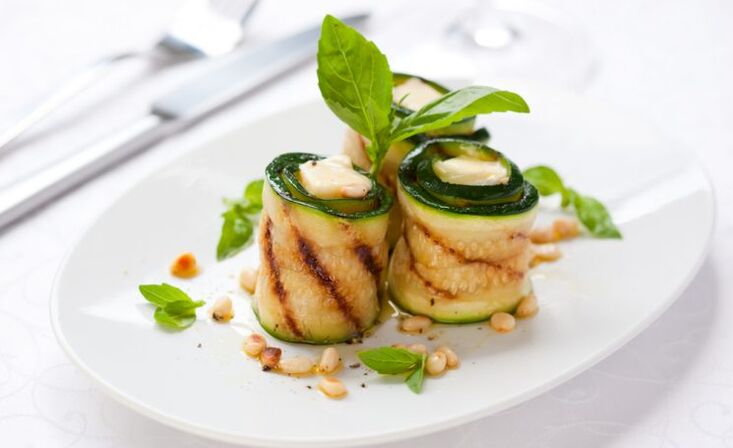

Ingredients:2 medium zucchini, 1/2 red bell pepper (without seeds), 1 cucumber, 100 g low-fat cottage cheese, 1 bunch arugula, 1 tbsp. l. olive oil, 1 dl. finely chopped fresh herbs, salt to taste.
Instruction.Wash zucchini, cut into thin lengthwise strips, sauté lightly on both sides with olive oil for 2 minutes each (can be baked in the oven). Mix cottage cheese with herbs, salt to taste. Cut the bell pepper and cucumber into thin lengthwise strips. Put some cottage cheese on the end of the zucchini strip. Add a few strips of pepper, cucumber, arugula leaves, roll up and place upright on a plate.
Curd casserole with apples
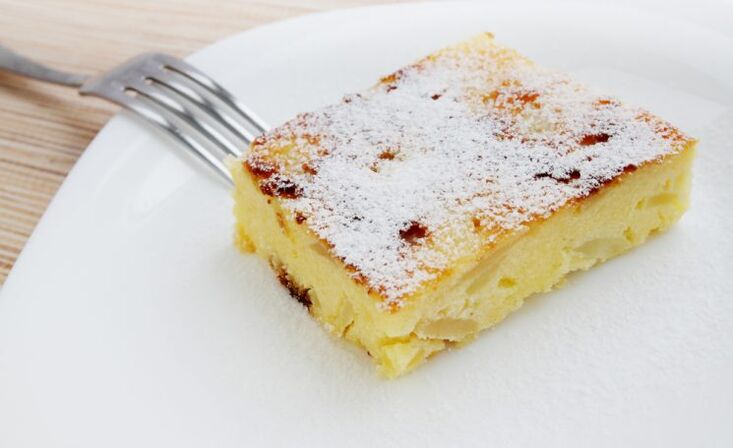

Ingredients:400 g fat-free cottage cheese, 2 eggs, 1 tsp. starch, 1/4 tsp. salt, 1 tbsp. l. Sugar, 2 Antonovka apples.
Instruction.Beat eggs with salt and sugar, add cottage cheese and starch. Peel the apples, remove the core, cut into small cubes and add to the mixture. Mix everything. Microwave for 12 minutes or oven until cooked through. Serve with yoghurt, honey or jam.
Quark dessert berry
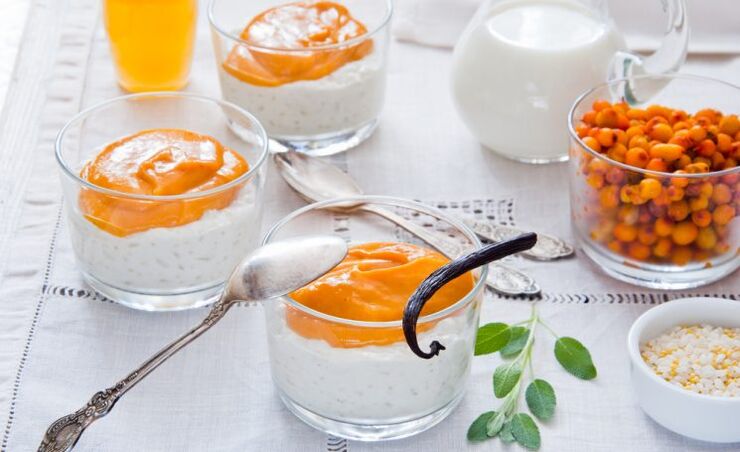

Ingredients:400 g low-fat cottage cheese, 100 g fresh berries, 2 egg whites, 1 tbsp. l. Sugar, 12 g gelatin, 1/4 packet vanillin.
Instruction.Soak the gelatine in 5-7 tablespoons of cold water. Whisk together the whites. Add vanillin, sugar to cottage cheese, add whipped proteins. Melt the gelatin over low heat until dissolved and add to the curd mass, whisk. Leave in the fridge for 5 hours and serve garnished with berries.